P1]
In today’s complex and data-rich environment, organizations are constantly seeking ways to leverage information for competitive advantage. While descriptive and diagnostic analytics provide insights into what happened and why, and predictive analytics forecasts future trends, prescriptive analytics takes it a step further. It doesn’t just predict what will happen; it recommends the best course of action to achieve desired outcomes.
Prescriptive analytics uses advanced techniques to analyze data, identify optimal solutions, and recommend specific actions that maximize profits, minimize costs, or achieve other strategic goals. It acts as a guide, helping decision-makers navigate uncertainty and make informed choices based on data-driven insights.
Understanding the Layers of Analytics
To appreciate the power of prescriptive analytics, it’s helpful to understand its place within the broader landscape of business analytics:
-
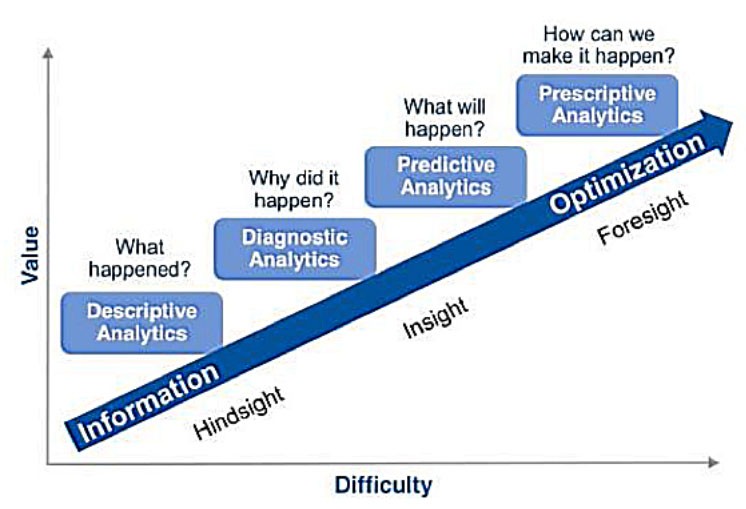
Descriptive Analytics: This is the foundation, summarizing historical data to understand past performance. Think of reports showing sales figures, website traffic, or customer demographics. It answers the question: "What happened?"
-
Diagnostic Analytics: This delves deeper, investigating the reasons behind past events. It aims to understand why something happened by analyzing relationships and patterns in the data. It answers the question: "Why did it happen?"

-
Predictive Analytics: This uses statistical models and machine learning to forecast future outcomes based on historical data and trends. It answers the question: "What will happen?"

Prescriptive Analytics: This builds upon the previous layers by recommending the best course of action to achieve a desired outcome. It answers the question: "What should we do?"
The Mechanics of Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive analytics employs a range of techniques to identify optimal solutions, including:

-
Optimization Algorithms: These algorithms aim to find the best possible solution from a set of alternatives, considering various constraints and objectives. Examples include linear programming, integer programming, and non-linear programming.
-
Simulation: This involves creating a virtual model of a real-world system and simulating different scenarios to evaluate their potential outcomes. This helps understand the impact of different decisions before they are implemented.
-
Decision Trees: These visual representations of decision-making processes help to analyze different options and their potential consequences, leading to informed choices.
-
Heuristics: These are rule-based approaches that provide practical solutions when optimization algorithms are too complex or time-consuming. They offer a good, albeit not necessarily optimal, solution.
-
Machine Learning: Specifically, reinforcement learning algorithms can be used to learn optimal strategies through trial and error, adapting to changing conditions and optimizing performance over time.
Applications of Prescriptive Analytics Across Industries
The applications of prescriptive analytics are vast and span across numerous industries:
-
Supply Chain Management: Prescriptive analytics can optimize inventory levels, routing logistics, and production schedules to minimize costs and improve efficiency. For example, it can determine the optimal quantity of each product to order, the best transportation routes to use, and the most efficient allocation of resources across different warehouses.
-
Marketing: It can optimize pricing strategies, personalize marketing campaigns, and allocate marketing budgets effectively. For instance, it can identify the optimal price point for a product based on demand elasticity, determine the most effective channels to reach target customers, and allocate marketing spend across different campaigns to maximize ROI.
-
Finance: Prescriptive analytics can optimize investment portfolios, manage risk, and detect fraud. For example, it can recommend the optimal asset allocation for a portfolio based on risk tolerance and investment goals, identify potential fraudulent transactions, and optimize lending decisions.
-
Healthcare: It can optimize patient care pathways, allocate resources efficiently, and improve patient outcomes. For example, it can determine the optimal treatment plan for a patient based on their medical history and condition, allocate hospital beds and staff efficiently, and predict patient readmission rates.
-
Retail: Prescriptive analytics can optimize pricing strategies, personalize product recommendations, and manage inventory effectively. For instance, it can determine the optimal price for each product based on demand and competition, recommend relevant products to customers based on their browsing history and purchase behavior, and optimize inventory levels to minimize stockouts and overstocking.
-
Energy: It can optimize energy production, distribution, and consumption. For example, it can optimize the operation of power plants, predict energy demand, and manage the grid effectively.
Benefits of Implementing Prescriptive Analytics
The benefits of implementing prescriptive analytics are significant and can translate into a competitive advantage:
-
Improved Decision-Making: By providing data-driven recommendations, prescriptive analytics helps decision-makers make more informed and effective choices.
-
Increased Efficiency: It optimizes processes and resource allocation, leading to greater efficiency and reduced costs.
-
Enhanced Profitability: By identifying opportunities for revenue growth and cost reduction, prescriptive analytics can significantly improve profitability.
-
Reduced Risk: It helps organizations identify and mitigate potential risks, minimizing losses and ensuring business continuity.
-
Competitive Advantage: By leveraging data to optimize decision-making, organizations can gain a competitive edge in the market.
Challenges in Implementing Prescriptive Analytics
Despite its potential, implementing prescriptive analytics can present several challenges:
-
Data Quality: Prescriptive analytics relies on high-quality, accurate, and complete data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to flawed recommendations.
-
Model Complexity: Developing and maintaining complex prescriptive models requires specialized skills and expertise.
-
Integration: Integrating prescriptive analytics into existing systems and processes can be challenging.
-
Change Management: Implementing prescriptive analytics requires a shift in mindset and a willingness to embrace data-driven decision-making.
-
Ethical Considerations: It’s important to consider the ethical implications of prescriptive analytics, ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability.
Overcoming the Challenges
To successfully implement prescriptive analytics, organizations should focus on:
-
Data Governance: Establishing robust data governance policies and procedures to ensure data quality and consistency.
-
Talent Acquisition: Investing in training and development to build a skilled team of data scientists and analysts.
-
Technology Infrastructure: Implementing a robust technology infrastructure that can support the development, deployment, and maintenance of prescriptive models.
-
Collaboration: Fostering collaboration between business users and data scientists to ensure that prescriptive models are aligned with business needs.
-
Iterative Approach: Adopting an iterative approach to implementation, starting with small-scale projects and gradually expanding to more complex applications.
Conclusion
Prescriptive analytics represents the pinnacle of business analytics, offering organizations the power to optimize decision-making and achieve desired outcomes. By leveraging advanced techniques to analyze data and recommend specific actions, it empowers businesses to navigate uncertainty, improve efficiency, enhance profitability, and gain a competitive advantage. While implementation can be challenging, the potential benefits are significant, making prescriptive analytics a critical tool for organizations seeking to thrive in today’s data-driven world. Embracing this powerful approach can transform data from a passive record of the past into an active driver of future success.
FAQ
Q: What is the difference between predictive and prescriptive analytics?
A: Predictive analytics forecasts what will happen in the future, while prescriptive analytics recommends the best course of action to achieve a desired outcome. Predictive analytics tells you what will happen, while prescriptive analytics tells you what to do about it.
Q: What are some common techniques used in prescriptive analytics?
A: Common techniques include optimization algorithms, simulation, decision trees, heuristics, and machine learning (particularly reinforcement learning).
Q: What industries can benefit from prescriptive analytics?
A: Many industries can benefit, including supply chain management, marketing, finance, healthcare, retail, and energy.
Q: What are the challenges of implementing prescriptive analytics?
A: Key challenges include data quality, model complexity, integration with existing systems, change management, and ethical considerations.
Q: How can organizations overcome these challenges?
A: Organizations can overcome these challenges by focusing on data governance, talent acquisition, technology infrastructure, collaboration, and an iterative approach to implementation.
Q: Is prescriptive analytics only for large companies?
A: While large companies often have more resources to invest in prescriptive analytics, smaller companies can also benefit from it. Cloud-based solutions and open-source tools make prescriptive analytics more accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Q: How do I get started with prescriptive analytics?
A: Start by identifying a specific business problem that can be addressed with prescriptive analytics. Then, assess your data availability and quality. Finally, build a team with the necessary skills or partner with a consultant to develop and implement a solution.
Q: What is the ROI of prescriptive analytics?
A: The ROI of prescriptive analytics can be significant, but it depends on the specific application and the effectiveness of the implementation. It can lead to increased revenue, reduced costs, improved efficiency, and reduced risk.
Q: How often should prescriptive models be updated?
A: Prescriptive models should be updated regularly to reflect changing business conditions and new data. The frequency of updates will depend on the specific application and the volatility of the data.
Q: What skills are required to work with prescriptive analytics?
A: Key skills include data analysis, statistical modeling, optimization, programming, and domain expertise in the relevant industry.
Leave a Reply