P1]
In today’s data-driven world, organizations are awash in information. However, this deluge of data often resides in disparate systems, leading to inconsistencies, inaccuracies, and ultimately, poor decision-making. This is where Master Data Management (MDM) steps in, offering a crucial framework for creating a single, reliable source of truth for your most critical business entities.
MDM is not just a technological solution; it’s a comprehensive strategy, a disciplined approach, and a set of processes aimed at managing, centralizing, and synchronizing master data across an organization. This article delves into the core principles of MDM, exploring its benefits, challenges, implementation strategies, and future trends.
What is Master Data?
Before diving into the intricacies of MDM, it’s crucial to understand what master data actually is. Master data refers to the core, non-transactional data that defines the key entities within an organization. These entities are typically categorized into:
- Customers: Information about your clients, including their names, addresses, contact details, purchase history, and demographics.
- Products: Details about the goods or services you offer, encompassing descriptions, specifications, pricing, and inventory information.
- Suppliers: Data related to your vendors, including their contact information, payment terms, and performance metrics.
- Locations: Information about your physical locations, such as offices, warehouses, stores, and manufacturing plants.
- Employees: Details about your workforce, including their names, roles, departments, and contact information.
- Assets: Information about the assets of the organization, including the details of their existence, location and maintenance.

These master data entities are foundational to virtually every business process, from sales and marketing to supply chain management and finance. The accuracy and consistency of this data are paramount to operational efficiency and strategic decision-making.
The Need for Master Data Management
Without a robust MDM strategy, organizations often suffer from a range of problems:
- Data Silos: Information is fragmented across different departments and systems, leading to inconsistencies and redundancies.
- Inaccurate Data: Duplicate, incomplete, or outdated data can lead to errors in reporting, analysis, and decision-making.
- Inefficient Processes: Data inconsistencies can cause delays, rework, and increased costs in various business processes.
- Poor Customer Experience: Inaccurate customer data can result in misdirected marketing campaigns, inaccurate billing, and frustrating customer service interactions.
- Compliance Issues: Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to regulatory compliance violations and potential penalties.
- Lack of a Single Source of Truth: Without a unified view of key business entities, it becomes difficult to make informed decisions and track performance effectively.

MDM addresses these challenges by providing a central repository for master data, ensuring consistency, accuracy, and accessibility across the organization.
Benefits of Implementing MDM
The benefits of implementing a well-designed MDM strategy are significant and far-reaching:
- Improved Data Quality: MDM ensures data accuracy, completeness, and consistency, leading to more reliable insights and better decision-making.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: By eliminating data silos and streamlining data processes, MDM reduces errors, rework, and costs.
- Better Customer Experience: Accurate customer data enables personalized marketing, improved customer service, and stronger customer relationships.
- Improved Decision-Making: MDM provides a single, reliable source of truth for key business entities, enabling more informed and data-driven decisions.
- Reduced Risk and Improved Compliance: Accurate and complete data helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements and mitigate risks.
- Increased Agility and Innovation: MDM provides a solid foundation for data analytics and innovation, enabling organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
- Streamlined Reporting and Analytics: Having a consistent and reliable source of data simplifies reporting and analytics, providing a clearer picture of business performance.
MDM Implementation Styles
There are several MDM implementation styles, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of implementation style depends on the specific needs and priorities of the organization:
- Consolidation Style (Registry Approach): This approach focuses on creating a central registry of master data, without physically moving or consolidating the data itself. The registry acts as a directory, providing pointers to the location of master data in different systems. This is useful for data governance and reporting.
- Centralized Style (Repository Approach): This approach involves physically consolidating master data into a central repository. This provides a single source of truth for all master data, but requires significant data migration and integration efforts.
- Coexistence Style (Hybrid Approach): This approach combines elements of both the consolidation and centralized styles. Master data is consolidated into a central repository for some entities, while other entities are managed through a registry approach.
- Transactional Style: This approach ensures that any changes made to master data are immediately reflected across all systems. This style is often used in industries where real-time data accuracy is critical.
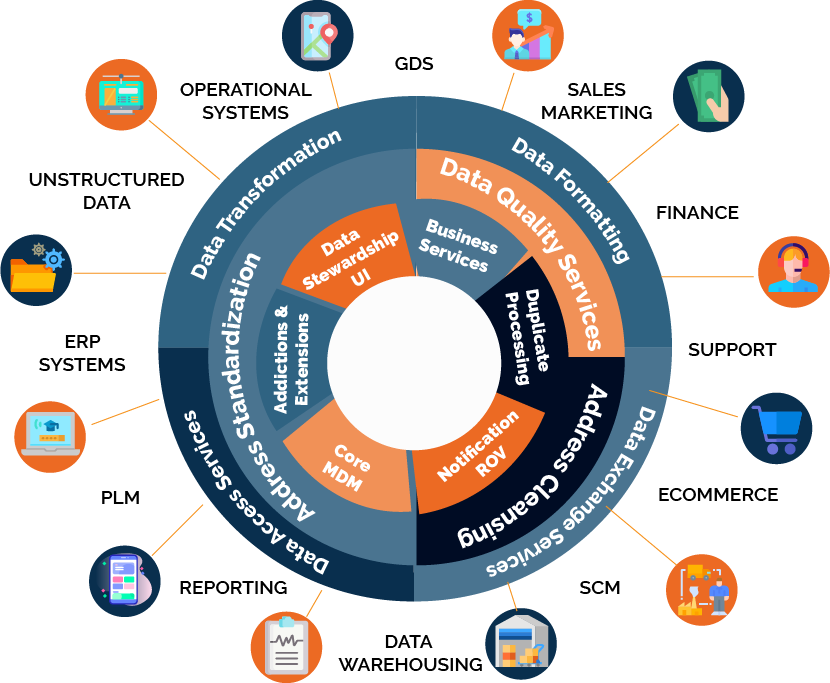
Key Components of an MDM Solution
A comprehensive MDM solution typically includes the following key components:
- Data Modeling: Defining the structure and attributes of master data entities, as well as the relationships between them.
- Data Integration: Connecting to various source systems and extracting master data for cleansing, matching, and consolidation.
- Data Cleansing: Identifying and correcting errors, inconsistencies, and duplicates in master data.
- Data Matching and Deduplication: Identifying and merging duplicate records across different systems.
- Data Governance: Establishing policies and procedures for managing master data, including data ownership, access control, and data quality standards.
- Workflow Management: Automating data management processes, such as data creation, modification, and approval.
- Data Security: Protecting master data from unauthorized access and modification.
- Reporting and Analytics: Providing insights into master data quality, usage, and impact on business performance.
- Data Stewardship: Assigning responsibility for data quality and governance to specific individuals or teams.
Challenges of Implementing MDM
While the benefits of MDM are significant, implementing a successful MDM strategy can be challenging:
- Complexity: MDM projects can be complex, requiring significant technical expertise and business process knowledge.
- Cost: MDM solutions can be expensive, requiring investments in software, hardware, and consulting services.
- Organizational Change: MDM requires significant organizational change, including changes to data governance policies, business processes, and roles and responsibilities.
- Data Quality Issues: Existing data quality issues can complicate the MDM implementation process.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist changes to data management processes, especially if they are accustomed to working with data silos.
- Lack of Executive Sponsorship: MDM projects require strong executive sponsorship to ensure buy-in and support from all stakeholders.
- Choosing the Right Technology: Selecting the right MDM technology for the organization’s specific needs can be challenging.
Best Practices for MDM Implementation
To overcome these challenges and ensure a successful MDM implementation, consider the following best practices:
- Start with a Clear Business Case: Define the specific business problems that MDM will address and quantify the potential benefits.
- Secure Executive Sponsorship: Obtain strong support from executive leadership to ensure buy-in and commitment from all stakeholders.
- Establish a Data Governance Framework: Define policies and procedures for managing master data, including data ownership, access control, and data quality standards.
- Focus on Data Quality: Prioritize data cleansing and data quality improvement efforts.
- Choose the Right Implementation Style: Select the MDM implementation style that best fits the organization’s needs and priorities.
- Involve Business Users: Engage business users throughout the MDM implementation process to ensure that the solution meets their needs.
- Use an Agile Approach: Adopt an agile approach to MDM implementation, breaking the project into smaller, manageable iterations.
- Measure and Monitor Progress: Track key metrics to measure the progress of the MDM implementation and identify areas for improvement.
- Provide Training and Support: Provide adequate training and support to users to ensure that they can effectively use the MDM solution.
Future Trends in MDM
The field of MDM is constantly evolving, with new technologies and approaches emerging all the time. Some of the key future trends in MDM include:
- Cloud-Based MDM: Cloud-based MDM solutions are becoming increasingly popular, offering greater scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- AI-Powered MDM: Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to automate data cleansing, matching, and governance tasks.
- Graph Databases: Graph databases are being used to model complex relationships between master data entities.
- Real-Time MDM: Real-time MDM solutions are enabling organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
- Data Fabric Architecture: MDM is becoming an integral part of the broader data fabric architecture, providing a consistent and unified view of data across the organization.
- Embedded MDM: MDM functionalities are being embedded directly into business applications, making data governance and quality an integral part of the workflow.
Conclusion
Master Data Management is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for organizations seeking to thrive in today’s data-driven environment. By establishing a single, reliable source of truth for your most critical business entities, MDM can improve data quality, enhance operational efficiency, improve customer experience, reduce risk, and enable better decision-making. While implementing MDM can be challenging, following best practices and staying abreast of emerging trends can help organizations unlock the full potential of their data and achieve a significant competitive advantage. The journey to mastering your data universe starts with a well-defined MDM strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between MDM and Data Governance?
A: While related, MDM and Data Governance are distinct. MDM focuses on creating and maintaining a single, consistent view of master data, while Data Governance encompasses the broader framework of policies, procedures, and responsibilities for managing all data assets within an organization. MDM is often a key component of a comprehensive Data Governance program.
Q: How long does it take to implement MDM?
A: The implementation timeline for MDM projects varies depending on the complexity of the project, the scope of the data, and the chosen implementation style. A simple MDM project might take a few months, while a more complex project could take a year or more.
Q: What skills are required for an MDM team?
A: An MDM team typically requires a mix of technical and business skills, including data modeling, data integration, data quality, data governance, business process analysis, and project management.
Q: What is the ROI of MDM?
A: The ROI of MDM can be significant, but it depends on the specific benefits realized by the organization. Potential ROI benefits include reduced costs, increased revenue, improved customer satisfaction, and reduced risk.
Q: How do I choose the right MDM solution?
A: Choosing the right MDM solution depends on the organization’s specific needs and requirements. Consider factors such as the size and complexity of the data, the required functionality, the integration capabilities, and the cost of the solution.
Q: Can I implement MDM in the cloud?
A: Yes, cloud-based MDM solutions are becoming increasingly popular, offering greater scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Q: What are the key metrics to track for MDM success?
A: Key metrics to track for MDM success include data quality metrics (e.g., accuracy, completeness, consistency), data usage metrics (e.g., number of users accessing master data), and business outcome metrics (e.g., reduced costs, increased revenue).
Q: Is MDM only for large enterprises?
A: No, MDM can benefit organizations of all sizes. While large enterprises may have more complex data landscapes, even small and medium-sized businesses can benefit from a well-designed MDM strategy.
Q: How do I get started with MDM?
A: The first step is to define a clear business case for MDM and secure executive sponsorship. Then, establish a data governance framework and assess your existing data quality. Finally, choose the right MDM solution and implementation style for your organization’s needs.
Q: What happens if my data sources change?
A: MDM solutions are designed to be flexible and adaptable to changing data sources. The data integration component of the MDM solution should be able to connect to new data sources and incorporate them into the master data model. Regular maintenance and monitoring are crucial to ensure the MDM system adapts to changes in the data landscape.

Leave a Reply